Design Notes: Push-Block on ROS Demo
This demo program is an extension of the push-block application that simulates a block being moved between 4 side channels involving the end-effector moving into the cavities. The application is now restructured as a client-server ROS design.
This demo program is based on the Push-Block Demo. The content covers the extended part only.
This demo requires the Panda robot model.
Running the Demo Program
Assume that the task trees and the arm commander packages are installed in a catkin_workspace. Refer to the Installation Guide
Change directory to the root of the catkin workspace, run
source devel/setup.bash.Change directory to this demo folder, run the ROS server first
/usr/bin/python3 ros_server.py.Then run the ROS client application
/usr/bin/python3 ros_demo.py.
Application Design based on the Task Trees Architecture
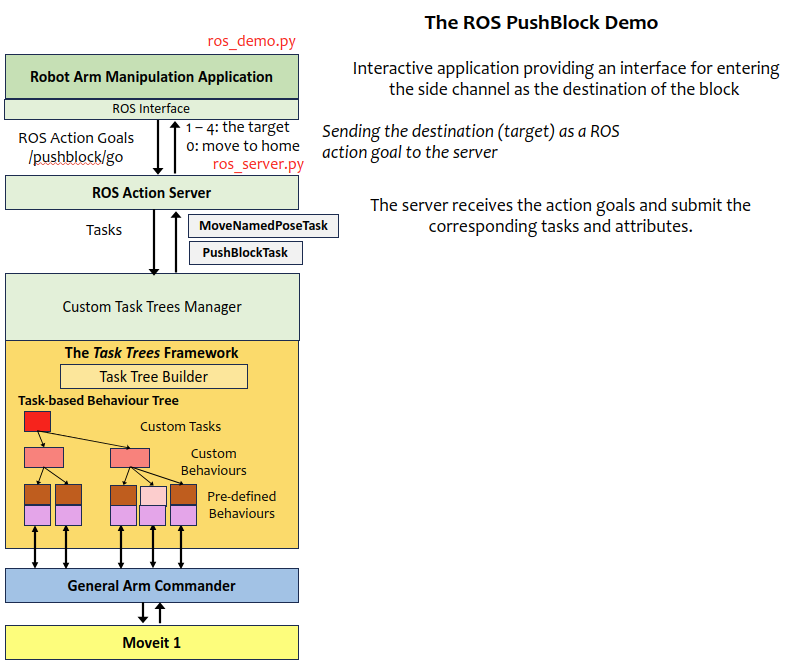
The majority of the application logic is now moved to the client ROS application (ros_demo.py). The key difference is sending ROS action goals to the ROS server instead of submitting tasks to the task trees manager.
The ROS server (ros_server.py) implements a hand-over mechanism, which receives goals from the clients and submit the corresponding tasks to the task trees manager.
The ROS action
The TaskAction is defined as follows.
### GOAL DEFINITION
int8 target
---
### RESULT DEFINITION
string data
---
### FEEDBACK DEFINITION
string data
The ROS server is listening at /pushblock/go for incoming goals. The target is an integer, and the range from 1 to 4 represents the destination area, and 0 represents moving to the home pose.
The Program Files
task_trees_manager_pushblock.py: defines the custom task trees manager, behaviour sub-trees for every task and the tasks.ros_server.py: implements the ROS action goal server, which receives a goal, submits the corresponding task, and handles goal abort and result return.ros_demo.py: implements the loop with interactive input, random target generation, and code for calling the ROS action goal server.task_scene.yaml: defines the positions and regions used in the application.